Badge
A small count and labeling component used to highlight information, statuses, or notifications, providing visual indicators for important data points.Basic Badge
The badge component can be created by calling the UI::badge() method.
Options
The Badge component can be customized using thebadgeOptions() method, it accepts multiple options at the same time.Badge::SOFT: Creates a badge with a softer, more subtle appearance using a light background and colored text.Badge::OUTLINE: Creates a badge with an outline style.Badge::ROUNDED: Creates a pill-shaped badge with fully rounded ends.Badge::CIRCLE: Creates a circular badge.Badge::BORDER: Creates a badge with a border.Badge::LABEL: Creates a badge styled as a label.
Badge Options Examples
Here are examples of each badge option to showcase their visual effect.Colored Badge
The bsStyle() method sets the color theme for the badge.
Soft Badge
The Badge::SOFT option creates a more subtle badge with a lighter background.
Outline Badge
The Badge::OUTLINE option creates a badge with an outline style.
Rounded Badge
The Badge::ROUNDED option creates a pill-shaped badge with fully rounded ends.
Circle Badge
The Badge::CIRCLE option creates a circular badge, often used for notification counts.
Border Badge
The Badge::BORDER option creates a badge with a border.
Label Badge
The Badge::LABEL option creates a badge styled as a label.
Combined Options
Multiple options can be combined using the bitwise OR operator (|).
API
The badge component extends fromHtmlElement so it has all its methods available.API PHP
Common alternative names: Tag, Chip, Label, Pill, Counter, Indicator, Status Indicator
Types: Default Badges, Soft Badges, Outline Badges, Rounded Badges, Circle Badges, Border Badges, Label Badges
Principles
Visual Emphasis
Badges draw attention to important information by using color, contrast, and positioning to make key details stand out within the interface.
Information Density
Badges efficiently communicate status, quantity, or category information in a small, compact form, allowing users to quickly scan and understand data.
Contextual Communication
Badges use color and shape conventions to convey meaning, making information immediately recognizable without requiring additional explanation.
Anatomy
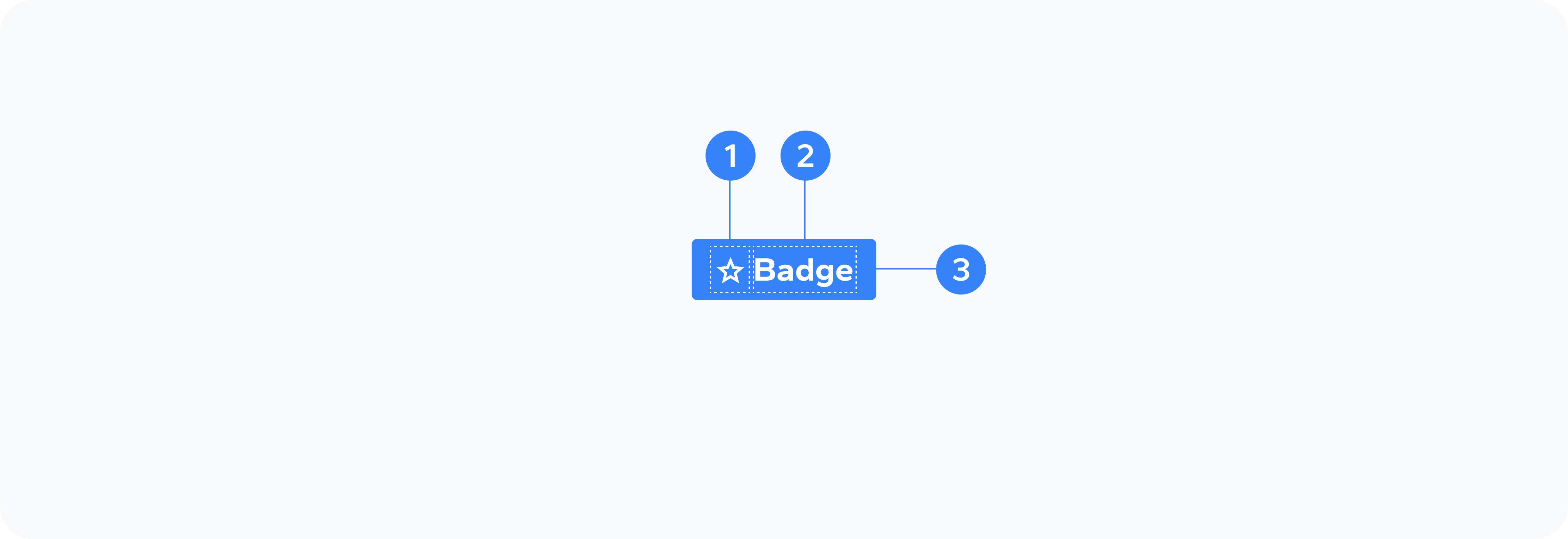
- Icon
- Content
- Container
Optional visual indicator that can be added to the badge
The main text or number displayed in the badge
The outer wrapper that holds the badge content
Usage
Use badges to highlight and draw attention to status, counts, labels, or notification indicators. They're particularly effective for displaying unread counts, status indicators, categorization tags, version numbers, and feature labels. Badges should be used sparingly to avoid overwhelming the interface, and their colors should follow a consistent system where each color has a specific meaning (e.g., red for errors, green for success).