Password Input
A specialized form input component that creates a password field with togglable visibility and enhanced security features.Basic Password Input
Creates a standard password input field with a name and placeholder.
Options
The Password component supports various configuration options.value: Initial password value (generally left empty for security reasons)placeholder: Placeholder text displayed when the input is emptyreadonly: Sets the input to read-only state (inherited from Input)disabled: Sets the input to disabled state (inherited from Input)required: Sets the input as required (inherited from Input)autocomplete: Controls browser autocomplete behavior (inherited from Input)
Password Input Examples
Here are examples of different ways to use the password input component.Password Input with Required Validation
Creates a required password input field.
Password Input with Label and Hint
Creates a password input with a label and hint text for password requirements.
Password Input with Custom Styling
Creates a password input with custom CSS classes.
Password Input with Autocomplete Off
Creates a password input with browser autocomplete disabled.
API
The password input component extends from theInput class so it has all its methods available.Common alternative names: Password Field, Secure Input, Protected Field, Secret Input, Masked Input, Security Field
Types: Basic Password, Toggleable Password, Strength Indicator Password, Confirmation Password, Multi-factor Password
Principles
Security
Password inputs prioritize security by masking input characters while providing the option to temporarily reveal content for verification. They balance security needs with user experience concerns.
Usability
Password fields offer clear affordances for password visibility toggling, helping users verify their input without compromising security in public settings.
Feedback
Modern password inputs provide visual feedback on password strength and requirement satisfaction, guiding users toward creating more secure passwords.
Anatomy
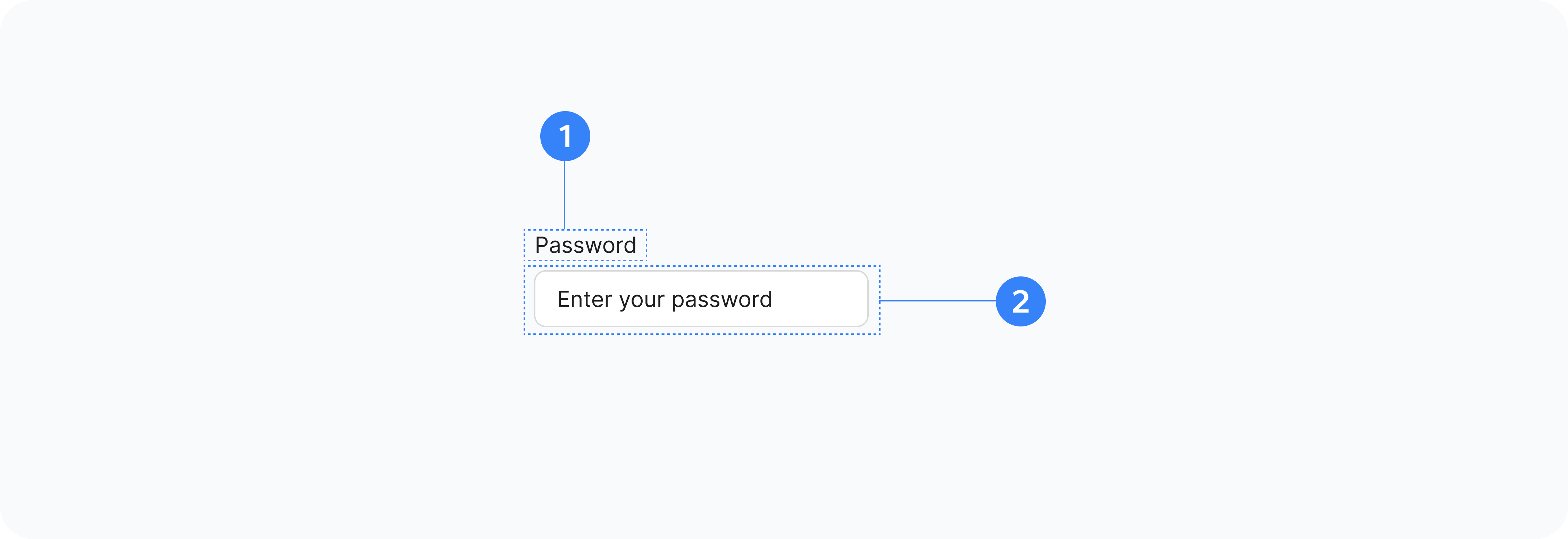
- Container
- Label
- Input Element
- Visibility Toggle
- Toggle Icons
- Hint
- Strength Indicator
Outer wrapper div that holds all elements
Optional text label describing the input's purpose
The actual password input field
Button to show/hide password text
Eye and crossed-eye icons indicating visibility state
Optional helper text providing password requirements
Optional visual feedback on password strength (when implemented)
Usage
Use password inputs for:
- User authentication
- Account creation
- Password changes
- PIN code entry
- Security question answers
- Access credentials
- Any sensitive text input that should be masked from view
Best Practices
- Never pre-fill password fields with actual passwords
- Provide clear password requirements to users
- Implement password strength indicators when appropriate
- Allow users to toggle password visibility
- Use appropriate autocomplete attributes for different contexts
- Consider implementing password managers compatibility
- Avoid password masking in contexts where privacy isn't a concern (e.g., on devices with no onlookers)
Common Patterns
Form Integration
- Login forms
- Registration forms
- Account management
- Security settings
- Password recovery
Security Features
- Password visibility toggle
- Password strength indicators
- Real-time validation feedback
- Password confirmation fields
- Password storage using proper encryption
User Interface
- Clean, simple design to emphasize security
- Clear affordances for password visibility
- Appropriate spacing to prevent misclicks
- Security-focused visual treatment
- Integration with password managers
Accessibility
- Use proper ARIA attributes (aria-label, aria-required, aria-invalid)
- Ensure keyboard navigation works with the visibility toggle
- Provide clear labels and instructions
- Ensure toggle button is fully accessible and has appropriate text alternatives
- Support screen readers by announcing password visibility changes
- Ensure error messages are programmatically associated with inputs