Tab
A component for switching between different content panels, providing a clean and organized way to display multiple sections of content without overwhelming the user interface.Basic Tabs
Create a standard tab interface with content panels.
Tab Options
The Tab component provides various customization options.- Different tab types (Tabs, Pills, Card Header, Arrow)
- Vertical tab layout
- Justified tabs with equal width
- Custom color styling
- Accessible keyboard navigation
Tab Examples
Here are examples of different tab options and styles.Pills Tabs
Create tabs with a pill-style appearance.
Vertical Tabs
Create tabs arranged vertically.
Justified Tabs
Create tabs that take up equal width.
Colored Tabs
Create tabs with custom color styling.
Card Header Tabs
Create tabs styled for use in card headers.
Arrow Navigation Tabs
Create tabs with arrow-style navigation.
API
The Tab component provides methods for creating and configuring tabs.API PHP
Events
You can listen to events on the GridJS component using the bouion() method.Common alternative names: Tab Panel, Tab Interface, Tab Navigation, Tabbed Interface, Tabbed Panel, Tabbed Navigation, Tab Container
Types: Default Tabs, Pill Tabs, Card Header Tabs, Arrow Tabs, Vertical Tabs, Justified Tabs, Colored Tabs
Principles
Visual Organization
Tabs organize content into clear, distinct sections while maintaining a clean and uncluttered interface.
Content Switching
Through clear visual indicators and consistent styling, tabs provide an intuitive way to switch between different content sections.
Context Preservation
Tabs maintain context while switching between different content panels, helping users understand their location in the interface.
Anatomy
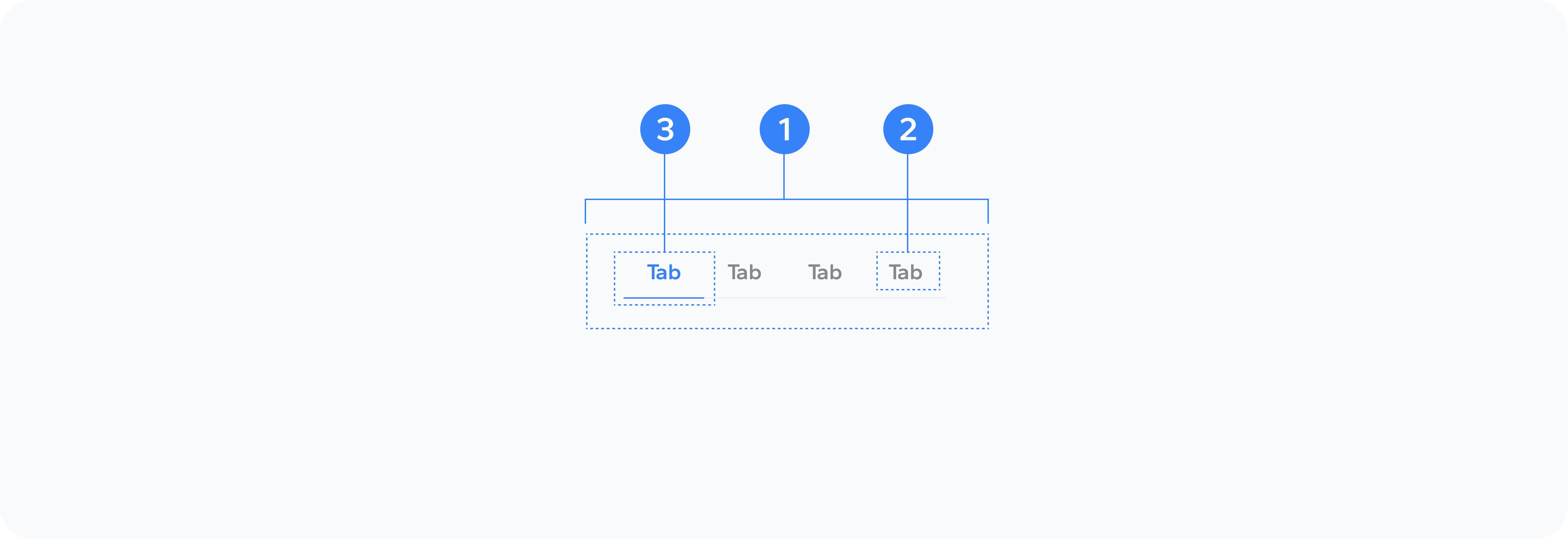
- Container
- Tab Element
- Active Tab Element
The outer wrapper that holds all tab content
The clickable tab headers
The active tab element
Usage
Use tabs to organize related content into distinct sections. They're particularly effective for:
- Content organization
- Feature grouping
- Settings panels
- Form sections
- Documentation
- Multi-step processes